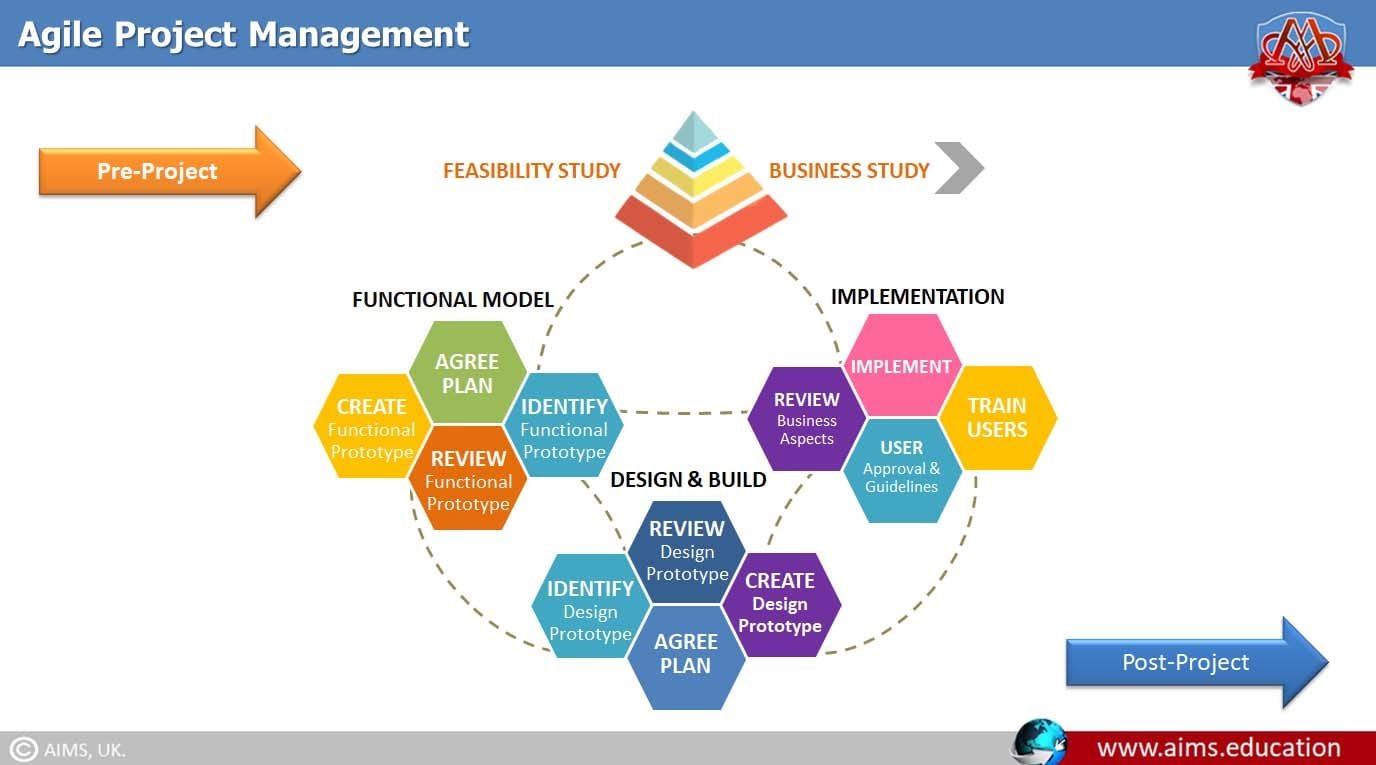
What is Agile Project Management?
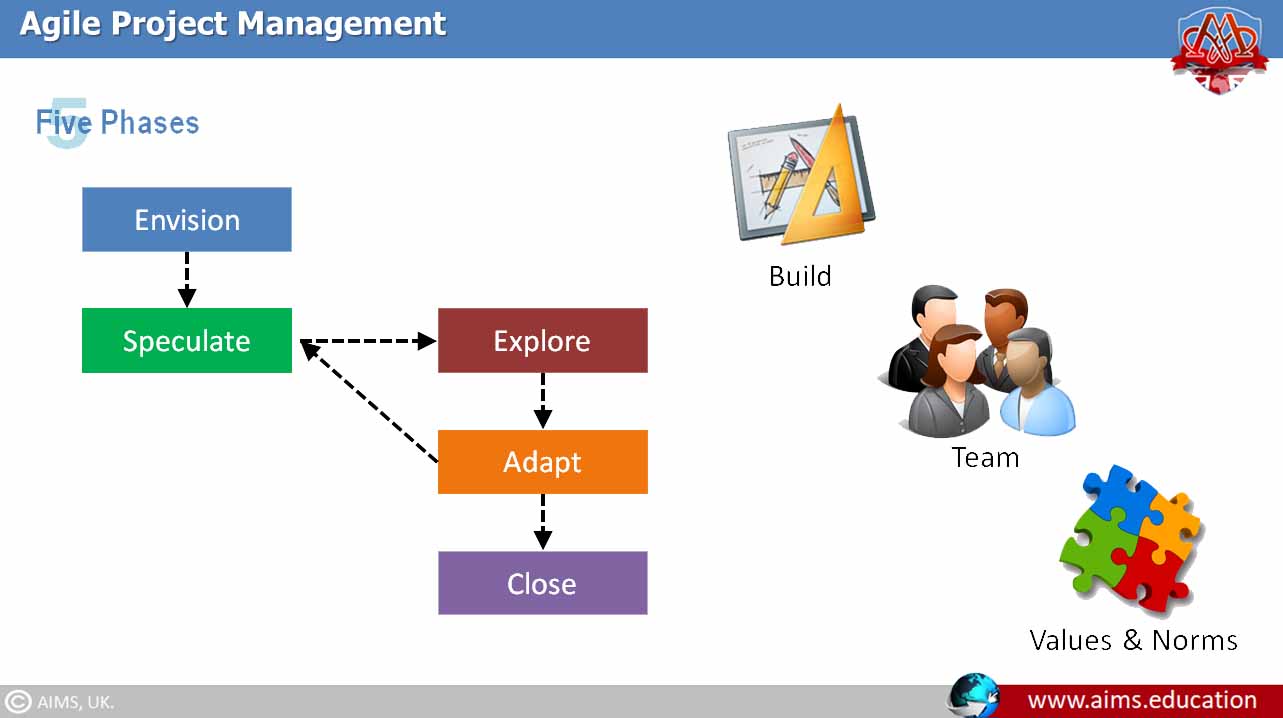
Agile project management is the process by which projects can be managed and implemented in small chunks of work. Agile projects deliver value to the business in frequent small deliveries of products called “Features”. In Agile PM, items are created by small logical chunks of work, and they are called “Iterations” or “Sprints”. Agile is a great technique to be used when business needs are frequently changing, or when they need to receive product benefits earlier. The agile project management framework is managed in five stages, and it is called the Agile Life Cycle. These phases are: Envision, Speculate, Explore, Adapt, and Close. The agile project management methodology is very different than the traditional waterfall methods.

Agile VS Waterfall Project Management
| Criteria | Agile Project Management | Waterfall Project Management |
| Approach | Iterative, adaptive approach with flexibility at its core. | Sequential, linear approach with rigid stages. |
| Project Lifecycle | Divided into sprints, encouraging constant evolution. | Divided into distinct phases, executed one after another. |
| Feedback Cycles | Short and continuous, allowing for frequent reassessment. | Limited and typically gathered at the end of the cycle. |
| Adaptation | Welcomes change at any point in the project’s progress. | Change is often considered a risk and discouraged. |
| Customer Involvement | High level of customer engagement with regular input. | Customer involvement is mainly at the beginning and end. |
| Scope | Flexible scope subject to adjustments as needed. | Fixed scope with limited room for deviation. |
| Risk Management | Embraces uncertainties, using them to steer improvements. | Attempts to identify all risks upfront, with less room for adjustments. |
Combining the best aspects of both Agile and traditional Waterfall methodologies, the Agile-Waterfall Hybrid model emerges as a robust strategy for managing complex projects. This approach allows for the detailed planning and structured phases of Waterfall to be integrated with Agile’s adaptability and customer focus.
Key Principles of the Agile Project Management Framework
- EMBRACES CHANGE: Agile frameworks are structured to accommodate and encourage changes, even late in the project, ensuring the final product is as relevant and value-driven as possible.
- INCREMENTAL DELIVERY: Products are built and delivered incrementally, rather than in one go, allowing for regular feedback and continuous improvement throughout the development cycle.
- CROSS-FUNCTIONAL TEAMS: Agile emphasizes the need for teams that consist of individuals with varied expertise working together towards a common goal, enhancing collaboration and innovation.
- CUSTOMER COLLABORATION: Regular customer input is integral, ensuring the development process aligns closely with clients’ needs and expectations.
- SIMPLICITY AND EFFICIENCY: Focuses on the art of maximizing the amount of work not done, simplifying processes, and delivering efficient solutions with minimal waste.
- CONTINUOUS EVALUATION: Teams continuously evaluate project performance against expected outcomes, thereby improving project quality and relevancy.
- ADAPTIVE PLANNING: Agile provides a flexible planning strategy that can tackle complexities and unpredictability, ensuring the project can pivot in response to emerging scenarios.
- SUSTAINABLE DEVELOPMENT: Promotes a pace and methodology that the team can sustain indefinitely, avoiding burnout and maintaining a high-quality output.
- REFLECTIVE IMPROVEMENT: Agile frameworks encourage constant reflection on successes and failures to continually improve processes and practices.
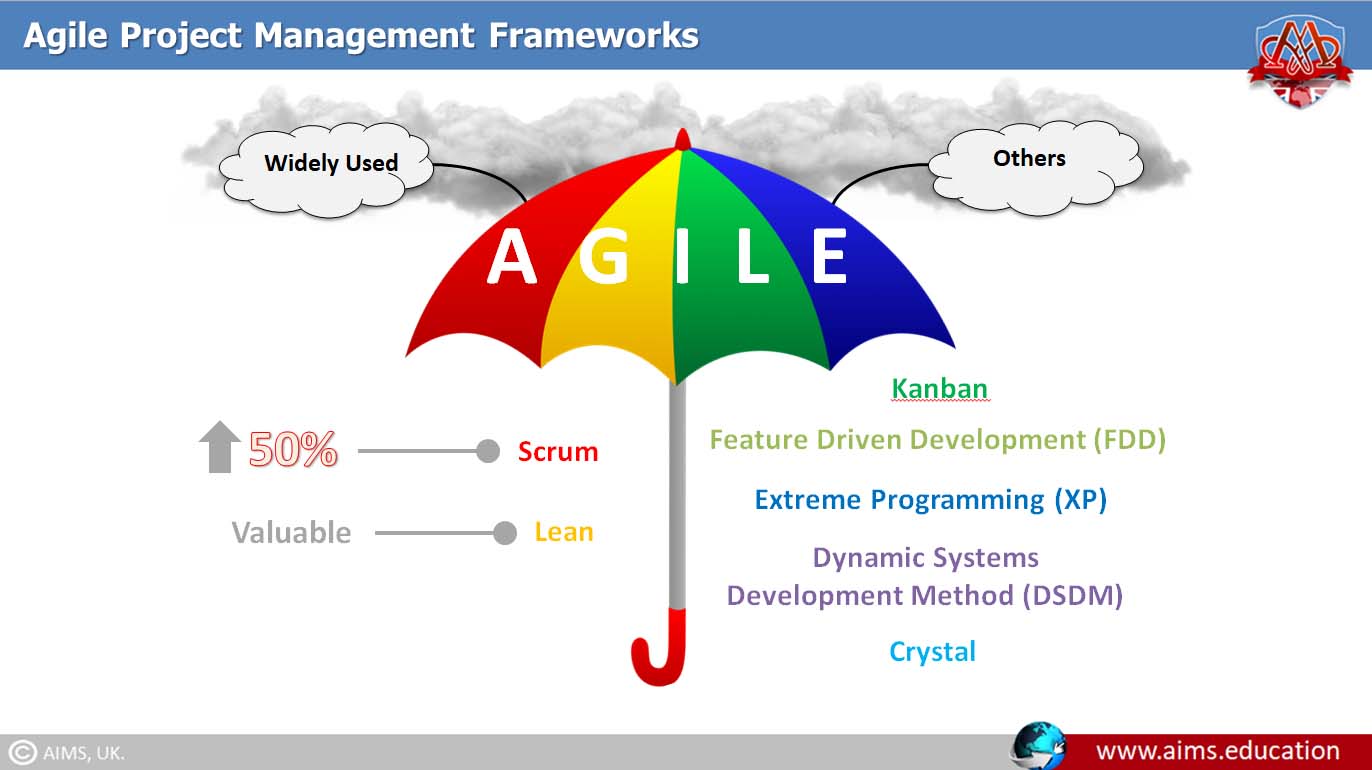
Agile Project Management Methodologies:
While Agile offers a broad philosophy for managing projects with flexibility and interactiveness, teams can adopt several specific methodologies within the Agile umbrella based on their unique needs. Each is characterized by its own set of principles, practices, and deliverables. Some of the most prominent Agile methodologies are Scrum, Kanban, Extreme Programming (XP), and Lean.
1. Scrum:
Scrum is particularly geared towards managing complex projects. It structures development in cycles of work called Sprints, with cross-functional teams working closely to reach defined goals. An example of Scrum project management is a software company implementing a bi-weekly Sprint to introduce new features to their application.
2. Kanban:
Kanban emphasizes continuous delivery without overburdening the project team. The key to Kanban is visualizing the work process on a Kanban board to balance demands with available capacity. For example, a marketing team uses a Kanban board to track the progress of campaign materials from ideation to publication.
3. Extreme Programming (XP):
Extreme Programming (XP) focuses on improving the quality of the project and addressing customer needs in a fast and flexible manner. It is characterized by frequent “releases” in short development cycles, which improves productivity and introduces checkpoints where new customer requirements can be adopted. For instance, a tech startup may use XP to iterate rapidly on their product, releasing updates weekly based on user feedback.
4. Lean:
Lean methodology, derived from Lean manufacturing principles, aims to shorten the production cycle by eliminating waste. This translates into delivering more value with fewer resources in project management. An example of Lean principles at work might be an eCommerce company analyzing its development pipeline to remove bottlenecks, thus streamlining its process to deploy faster updates to the shopping platform.
AGILE PROJECT MANAGEMENT WITH SCRUM: The Sprint to Success
Scrum is one of the most widely adopted agile project management methodologies. It introduces a structured framework for Agile project activity, accentuating the importance of roles, events, and artifacts.
1. THE SCRUM FRAMEWORK
In Scrum, the project work is divided into time-bound iterations called sprints, which usually last from one to four weeks. Each sprint includes a planning session, daily stand-up meetings, a review of what has been completed, and a retrospective to analyze what went well and what could be improved.
2. THE SCRUM MASTER AND PRODUCT OWNER
A successful Scrum team is led by a Scrum Master, who acts as a facilitator and coach for the team, and a Product Owner, who represents the stakeholders’ interests and guides the team to deliver value.
3. SPRINTS, RETROSPECTIVES, AND CONTINUOUS IMPROVEMENT
Sprints are more than just dividers of time; they are a journey of incremental development, a cycle of continuous delivery and feedback, feeding into the Agile commitment to relentless improvement.
Decoding the Agile Project Management Process
While Agile principles and values provide the foundation, the real meat lies in understanding the Agile project management process—how projects are managed from inception to completion.
The Agile Journey: A Bird’s Eye View
Agile projects typically proceed through five main phases: initiation, planning, execution, monitoring and controlling, and closure. Within each of these phases, Agile teams work differently than traditional project management, focusing on iterations, fluidity, and being adaptive.
Agile Project Management Phases
Agile projects are managed in five phases, called the Agile Life Cycle. These agile project management phases are Envision, Speculate, Explore, Adapt, and Close. Each phase of the Agile project management process plays a critical role in project success. The initiation phase sets the groundwork, planning establishes a roadmap, execution involves the development sprints, monitoring and controlling keep the project on track, and closure ensures that all deliverables meet the intended purpose.
Step-1: Initiating an Agile Project (Envasion)
Initiation is the preplanning stage where the project vision is set, and teams are assembled. Meticulous planning ensures that the project aligns with business objectives and that teams understand their roles and responsibilities.
Step-2: Agile Project Planning (Speculate)
The Agile planning phase is iterative and flexible, typically involving the creation of a product backlog, sprint planning, and assignment of tasks based on team velocity.
Step-3: Agile Project Execution (Explore)
The execution phase in Agile is characterized by short development cycles or sprints, during which teams work to deliver a set of prioritized features or functionalities. Frequent stand-up meetings are held for quick updates and to address any impediments.
Step-4: Monitoring and Controlling the Agile Process (Adapt)
Agile’s iterative nature necessitates a constant feedback loop. The monitoring and controlling phase involves tracking progress, communicating regularly with stakeholders, and making adjustments based on performance and customer feedback.
Step-5: Agile Project Closure (Close)
As the project nears completion, the Agile team focuses on delivering the final product increment and ensuring that all loose ends are tied. This phase includes final testing, documentation, and the handover to operations or next steps.
Agile Project Management Examples
As we embrace the Agile project management methodology, let’s highlight two real-world examples where Agile project management principles have been successfully implemented:
1. IBM’s Hybrid Agile Approach:
IBM has adopted a hybrid Agile model to deliver complex, multi-dimensional projects across its international teams. By combining both Scrum and Kanban methods, IBM tailors Agile principles to fit the varied requirements of its vast array of clients and projects. They employ Agile management tools to maintain visibility and coordination among teams, demonstrating the flexibility of Agile in managing large-scale projects efficiently and effectively.
2. Google’s Small Team Approach:
While Google operates at an incomparable scale, it adopts Agile project management through its focus on small team structures, known as “Project Oxygen.” This approach ensures that despite its size, teams within Google are nimble and able to innovate rapidly. Their philosophy advocates for the empowerment of each team, encouraging them to self-organize and make decisions quickly in alignment with Agile principles, leading to efficient product development and a strong culture of collaboration.
Best Agile Project Management Software and Tools
The landscape of Agile project management tools is diverse, offering a range of functionalities to meet the different needs of teams and projects. Here are five of the best Agile project management software and tools that have been well-received in the industry:
1. Jira Software:
Atlassian’s Jira is a household name in Agile project management. It’s designed specifically for software development teams to plan, track, and release great software. Jira comes with a suite of Agile tools, from Scrum and Kanban boards to detailed reporting features, and integrates seamlessly with other Atlassian products.
2. Trello:
Trello’s card/board solution is popular among Agile teams for its simplicity and flexibility. It provides a visual way to manage projects and tasks with drag-and-drop functionality. It’s particularly well-suited for small to medium-sized teams that need a straightforward tool to adapt to their changing needs.
3. Asana:
Asana is a task and project management tool that scales from individual tasks to strategic initiatives. Agile teams appreciate Asana for its versatility in project visualization (list, board, calendar views) and extensive integration capabilities, fostering a centralized workflow.
4. Monday.com:
Monday.com offers a highly customizable interface that can accommodate various Agile project management methodologies. With its ability to streamline processes and provide clear-eyed tracking of project progress through visual timelines, Monday.com is appreciated for its user-friendly design and powerful automation features.
5. VersionOne:
VersionOne is built specifically for enterprise software development and supports a full range of Agile and DevOps processes. As an all-in-one solution, it offers centralized project management, collaboration, and tracking of releases, sprints, and teams’ progress, suitable for organizations that manage complex product portfolios.
Earn Agile Expertise as a Competitive Edge in Business
Agile project management benefits professionals seeking to enhance their project management qualifications and expertise in a dynamic business landscape. By emphasizing flexibility and iterative progress, Agile methodologies align with principles taught in Online MBA Project Management programs, where innovative strategies and leadership skills are honed. Additionally, obtaining a Project Management Certificate grounded in Agile practices marks a pivotal step in demonstrating a commitment to excellence and continuous improvement in the field, providing individuals with a competitive edge and organizations with the assurance of best practices in managing and executing projects.
