What is Project Management?
In today’s fast-paced and ever-changing business landscape, project management has become an essential skill for any organization or individual looking to achieve their goals. To begin, we should delve into the question, “What is project management?”. In simple terms, it is the process of planning, organizing, executing, and monitoring a project from start to finish. It involves coordinating resources, tasks, and people to achieve specific objectives within a set timeframe and budget. At its core, what is project management but the art and science of driving a project from inception to conclusion, ensuring efficient use of resources, risk mitigation, and successful achievement of end goals.

What is a Project?
A project is a temporary endeavor undertaken to create a unique product, service, or result. It is distinguished by its clear objectives, defined start and end times, scope of work, and resources allocated. Each project is a microcosm that encapsulates its own aims and objectives, which are meticulously crafted to align with the strategic goals of the organization. It is important to note that:
- The temporary nature of projects indicates that it has a definite beginning and end.
- Every project creates a unique product, service, or result.
Project Management Definition:
Project management is a critical skill set in today’s fast-paced business environment. The project management definition encapsulates the essence of steering a project from inception to completion. It involves meticulous planning, organizing resources, directing personnel, and controlling operations to ensure project objectives are fulfilled efficiently and effectively.
What are Project Objectives and Purpose?
Project objectives are the specific, measurable outcomes that are expected to be achieved through the implementation of a project. They serve as the cornerstone upon which all planning and execution is built, providing direction and a clear set of goals to aim for.
1. SOLVE A SPECIFIC PROBLEM:
Every project embarks on a journey to address a particular challenge or need within the organization or the market. The objective is to develop a solution that is both effective and sustainable.
2. DELIVER VALUE:
Whether it’s through creating a new product, improving a process, or innovating a service, a central project objective is to deliver measurable value to stakeholders.
3. MEET STAKEHOLDER REQUIREMENTS:
A project strives to fulfill the requirements laid out by its stakeholders, balancing their diverse interests with the project’s capabilities and limitations.
4. FINISH ON TIME:
Adhering to the set timeline is critical. A key project objective is to reach the finish line within the predetermined schedule to achieve the intended benefits.
Project Examples:
The spectrum of project management covers an extensive array of endeavors, each varying in scope, complexity, and impact. Their timespan may be as fleeting as a single day or as extended as several years of dedication. Here are ten examples that illustrate the breadth of possible projects:
- Home Renovation: A personal project that involves redesigning or refurbishing parts of a home.
- Website Launch: A technical project aimed at creating and launching a brand’s online presence.
- Community Garden: A local initiative that focuses on sustainable living and community involvement.
- Marketing Campaign: A strategic project to promote a product or service and increase market share.
- Software Development: This involves creating a new application or system to address specific user needs.
- Organizational Restructuring: A corporate project aimed at improving efficiency and effectiveness within a company.
- Urban Development Plan: A large-scale civic project focused on city planning, infrastructure, and public amenities.
- Research and Development (R&D): They are centered around innovation, typically in technological or pharmaceutical fields.
- National Health Initiative: A government-led project targeting public health challenges on a national scale.
- International Space Station (ISS) Expedition: An expansive, multi-national scientific project with objectives that further humanity’s understanding of space.
Objectives of Project Management:
At its core, the objective of project management is to propel a project to its successful conclusion, while adhering to predefined performance parameters. Here are the pivotal objectives that delineate the purpose of project management:
1. LEADERSHIP AND TEAM MANAGEMENT:
Effective leadership and cohesive team management are key objectives that drive project success. Project managers are expected to inspire, lead, and maintain team dynamics, aligning individual capabilities and efforts toward the collective aim.
2. TIME MANAGEMENT AND MEETING DEADLINES:
Ensuring that projects adhere to set timelines is a fundamental objective. Time management within project management involves careful scheduling and monitoring progress to ensure deadlines are met, therefore upholding the integrity and credibility of the project delivery.
3. ADAPTABILITY AND PROBLEM-SOLVING:
The objective of adaptability is to navigate the inevitable uncertainties of projects and to cultivate a problem-solving mindset. This involves agile adaptation to new scenarios, pivoting strategies when required, and resolving issues with creativity and efficiency.
4. EFFECTIVE RESOURCE ALLOCATION:
The objective of meticulous resource allocation is to utilize human, financial, and physical resources optimally. By allocating resources wisely, project managers can ensure that every aspect of the project is adequately resourced, enhancing efficiency and preventing bottlenecks.
5. STRATEGIC PLANNING AND EXECUTION:
PM is fundamentally centered on strategic planning and execution. The objective is to meticulously plot the course of action before initiating a project, and then to steer it with precision, adapting to changes with resourcefulness and strategic foresight to meet all defined objectives.
6. RISK ASSESSMENT AND MITIGATION:
Identifying potential risks and proactively laying out mitigation strategies is a crucial objective of project management. The aim is to foresee challenges and plan contingencies, thus minimizing disruptions to the project’s progression and safeguarding its outcomes.
7. CONTINUOUS COMMUNICATION:
One of the pivotal PM objectives is to ensure clear, continuous communication among all stakeholders. This involves articulating the vision, updates, and changes effectively, fostering an environment of transparency and trust that is conducive to successful project completion.
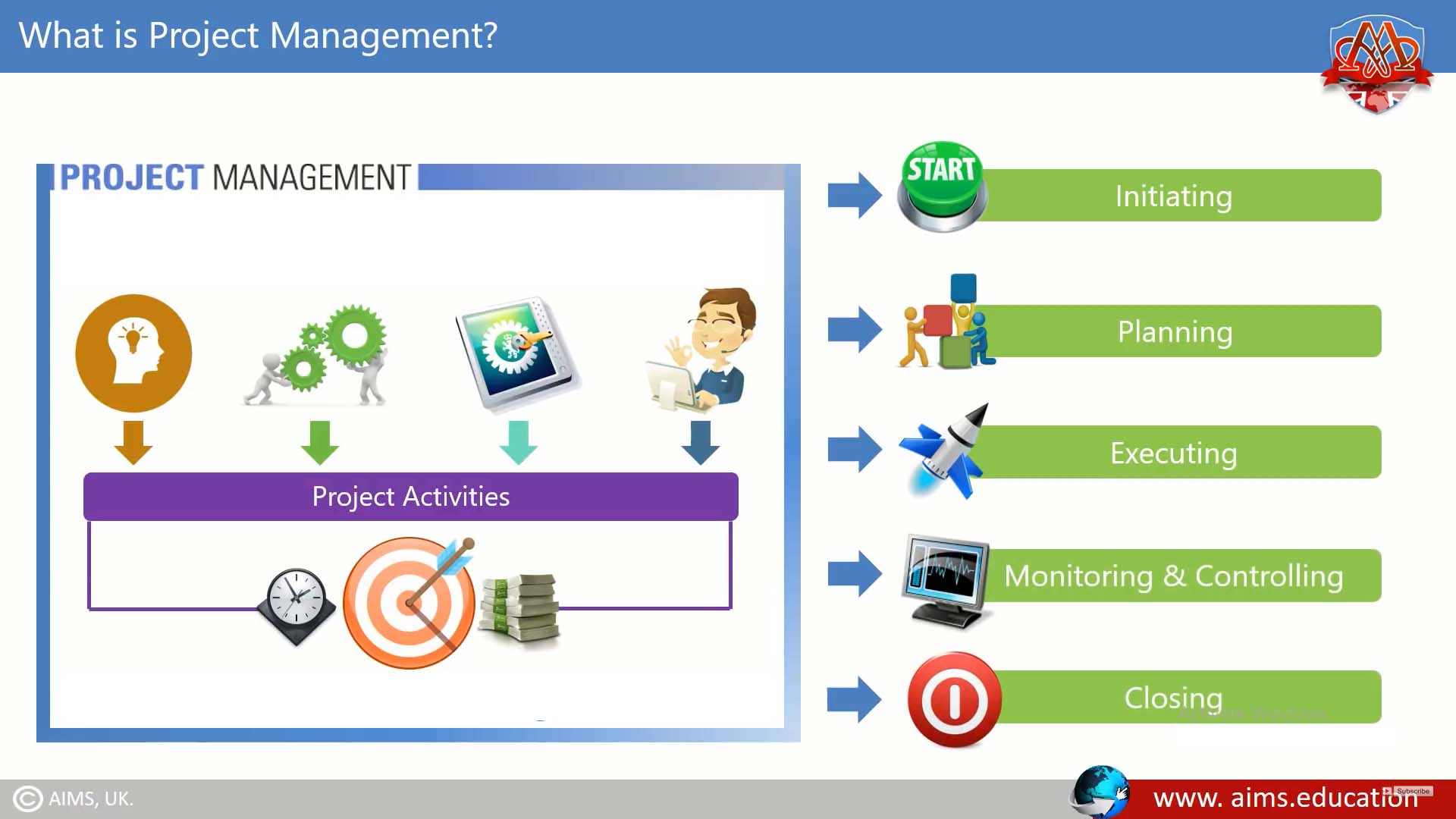
Project Management Phases:
PM activities can be broken down into key phases that map out the journey from conception to completion. These project management phases represent the lifecycle of a project and include:
- Initiation: This is the birth of the project where objectives are defined. It answers the fundamental question of ‘how to start a project and its purpose?‘ and ensures alignment with business goals.
- Planning: Often considered the backbone of PM, this phase is where a detailed project plan is developed, encompassing the scope, resources, timeline, and procedures for execution.
- Execution: The execution phase breathes life into the project plan, as the team carries out the tasks and activities needed to meet the project’s objectives.
- Monitoring and Controlling: Concurrent with execution, this phase involves tracking the progress to ensure it stays on course.
- Closing: In this final phase, the project is formally closed and delivered to the client or stakeholder.

4 Types of Project Management Methodologies
PM is an intellectual pursuit with a plethora of methodologies tailored to different kinds of projects and teams. Among them are four prominent types: Waterfall, Agile, Kanban, and Scrum.
1. WATERFALL: Systematic Sequential Approach
The Waterfall method is a linear project management model where each phase must be completed before the next one begins. It is characterized by its systematic sequence, which simplifies task scheduling and progress tracking.
2. AGILE: Flexibility and Incremental Delivery
Agile project management thrives on adaptability and customer collaboration, delivering work in small, consumable increments. Software development teams often leverage Agile methodologies.
3. KANBAN: Visual Workflow Management
Kanban is a highly visual method focusing on continuous delivery without overburdening the team. It utilizes a Kanban board—a tool that depicts work at various stages of the process using cards to represent tasks and columns to reflect each stage of the workflow.
4. SCRUM: Iterative Approach for Complex Projects
Scrum project management is an iterative framework within the Agile methodology that uses fixed-length iterations called sprints, typically lasting two to four weeks. It allows teams to break the work into manageable chunks and re-prioritize tasks as needed.
Importance of Project Management in Organizational Success:
PM is a critical driver of business success and organizational efficiency. At the heart of this discipline lies the capability to turn visionary ideas into tangible achievements through meticulous planning, strategic execution, and steadfast governance.
1. STRATEGIC BLUEPRINT OF PROJECT MANAGEMENT:
PM carves the path to corporate aspirations by establishing clear and reachable project objectives. The articulation of these objectives is more than mere goal-setting; it’s the strategic design of a blueprint that guides every stage of project development, ensuring that all resources, efforts, and actions are in harmony
2. INTERSECTION OF ART AND SCIENCE IN PROJECT MANAGEMENT:
Furthermore, adept project management navigates the complexities of interdepartmental dynamics, thereby fostering synergy across diverse functional units. This confluence of coordination and execution turns potential chaos into structured progression, enabling businesses to thrive amidst the turbulence of constant change.
3. PROJECT MANAGEMENT AS THE CORPORATE COMPASS:
In a world where change is the only constant, PM provides the stabilizing force that aligns projects with strategic business goals. It is this pivotal role of steering projects to success, while mitigating risks and ensuring stakeholder engagement, that underlines the unequivocal importance of PM in the contemporary corporate theater.
Evolution of Project Management in the Global Arena:
As we contemplate the trajectory of PM, it’s evident that the discipline is undergoing a dynamic evolution, shaped by globalization and technological innovation. The proliferation of online project management courses is democratizing access to knowledge, enabling aspiring professionals worldwide to acquire project management qualifications in the UK from the comfort of their homes. Similarly, advanced programs such as an online MBA in project management are crafting the next generation of leaders who are versed in both the theoretical underpinnings and practical applications of the field.
With these advancements, the future of project management promises not only a heightened emphasis on efficiency and adaptability but also a broadened scope for creative problem-solving and strategic leadership. Such qualifications are becoming indispensable in the corporate sphere, positioning PM at the forefront of business practices poised for continued growth well into the future.
